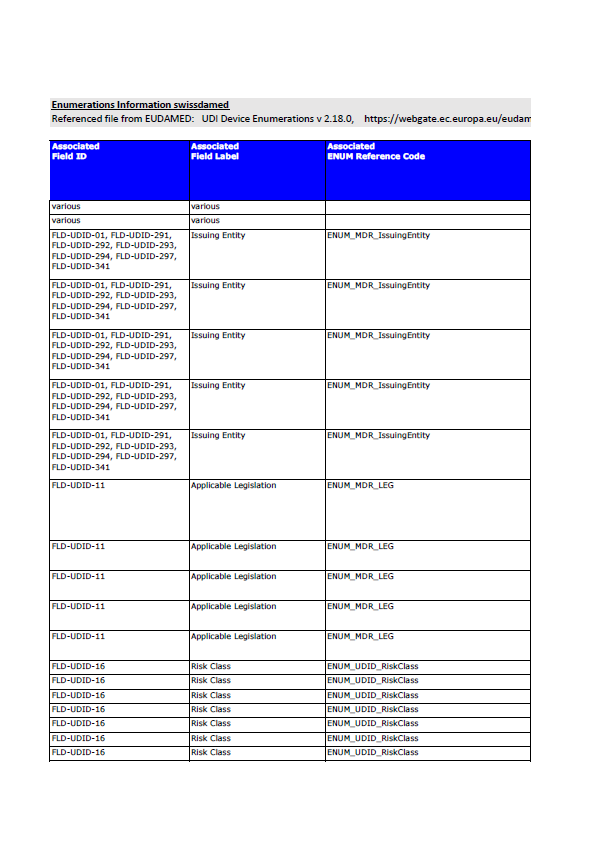
Swissmedic Publishes Updated EUDAMED UDI Enumerations: What Manufacturers Should Know
Swissmedic publishes updated EUDAMED UDI enumerations (v2.18.0). What this means for manufacturers preparing UDI, device and certificate data submissions.
EU-U.S. Data Privacy Framework Updated: What It Means for Medical Device Manufacturers
New EU-U.S. Data Privacy Framework FAQ impacts data transfers to U.S. vendors. What this means for medical device manufacturers in 2026.
FDA Publishes Final Guidance on Computer Software Assurance: Key Implications for Manufacturers
The FDA has released its final guidance on Computer Software Assurance (CSA) for production and quality system software, introducing a risk-based, streamlined approach to validating software used in manufacturing and quality operations. The updated framework helps manufacturers reduce unnecessary documentation, focus validation efforts on functions that impact product quality and patient safety, and accelerate the adoption of automated and digital technologies while remaining fully compliant with FDA requirements.
FDA Issues Updated Scientific Recommendations for Biosimilars: What Manufacturers Need to Know
The FDA has issued a new draft guidance that updates the scientific principles for demonstrating biosimilarity. The document clarifies when strong analytical similarity data, supported by comparative human pharmacokinetic and immunogenicity assessments, may be sufficient to demonstrate biosimilarity without requiring a comparative clinical efficacy study. This updated approach can help manufacturers reduce development timelines and costs, while placing greater emphasis on robust analytical packages, sensitive PK study designs and a clear, risk-based justification aligned with FDA expectations.
MDCG 2019-11 Rev.1 - New guidance on qualification and classification of software as a medical device or in vitro diagnostic medical device
The new revised version of the MDCG 2019-11 (Rev.1) clarifies the qualification and classification of software as a medical device (MDSW ) and in vitro diagnostic software (IVD), in the context of the MDR and IVDR. The document covers classification rules, integration with AI Act and EHDS, and includes practical and up-to-date examples. Smart MDR supports MDSW manufacturers in managing compliance and technical documentation.
UK publishes new model periodic safety report (PSUR) for medical devices - MHRA 2024
The MHRA has published a new Periodic Safety Update Report (PSUR) template for medical devices in the UK, in line with the UK MDR. The document details how manufacturers should structure their post-market monitoring (PMS) reports, including performance data, surveillance, PMCF and benefit-risk profile analysis.
Health Canada publishes new guidelines on the use of technical standards to demonstrate compliance with the Medical Devices Regulations
In January 2025, Health Canada published a new guide on the use of recognized standards to demonstrate compliance with the requirements of the Medical Devices Regulations. The document guides manufacturers in preparing submissions, updates and lifecycle management of applicable standards.
IMDRF Presents Playbook for Evaluating Medical Devices Based on Artificial Intelligence
The IMDRF has published a Playbook for the evaluation of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML) medical devices, addressing safety, efficacy and regulatory requirements. Global harmonization of these medical devices is essential to ensure transparency, reliability and compliance.
Government response to consultation on Medical Devices Regulations: EU law assimilated
The MHRA has confirmed that four key EU regulations for the regulation of medical devices and in vitro diagnostic medical devices (IVDs) will be retained in the UK after May 26, 2025. The decision covers rules on common technical specifications, electronic instructions for medical devices, the use of tissues of animal origin and the supervision of approved bodies. In addition, the MHRA plans to update the legislation, replacing the reference to Regulation (EU) 207/2012 with the more recent Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/2226. Meanwhile, further changes are expected with the upcoming "Pre-Market" legislation, which could impact the requirements for high-risk IVDs and remove temporary approvals for COVID-19 testing. Manufacturers and companies in the sector should follow these updates to ensure regulatory compliance in the UK market.
New IEC 62304 Revision Proposal: What Changes for Healthcare Software?
The proposed revision of IEC 62304 brings important changes for the development of software for medical devices and other healthcare applications. The new version expands the concept of Health Software to include solutions that assist in health management and monitoring, even without being classified as medical devices. Among the main changes are the simplification of the classification of software rigor, the removal of specific Quality System requirements and the revision of Risk Management, which no longer requires ISO 14971. In addition, the approach to legacy software will be reformulated, with guidelines transferred to an informative annex. As this update is still in the proposal stage, manufacturers should keep an eye on the changes and prepare for future adaptations.
MDCG 2025-1: Procedure Form for Updating the European Medical Device Nomenclature (EMDN)
MDCG 2025-1 introduces an ad hoc procedure form to facilitate the updating of the European Medical Device Nomenclature (EMDN). This document is crucial for manufacturers, national competent authorities (NCAs) and notified bodies (NBs) that need to register devices in the UDI-DI module of EUDAMED. The new approach allows proposals for new codes to be submitted when existing ones are insufficient, promoting the registration of innovative technologies and regulatory compliance. This initiative by the Medical Device Coordination Group (MDCG) contributes to standardisation and clarity in the medical device sector in the European Union.
MDCG 2024-2 Rev.1: Revolution in the European Medical Device Nomenclature
MDCG 2024-2 Rev.1 ushers in a new era for the European Medical Device Nomenclature (EMDN), establishing dynamic procedures that ensure innovation, safety, and efficiency in the medical device sector. This revision, aligned with the MDR and IVDR regulations, introduces annual updates and ad-hoc requests to meet rapid technological changes and growing market demands. With a focus on collaboration between stakeholders, the update reinforces trust between manufacturers, healthcare professionals and patients, ensuring that device classification is accurate, relevant and safe.