FDA Implements Updated Medical Device Inspection Compliance Program
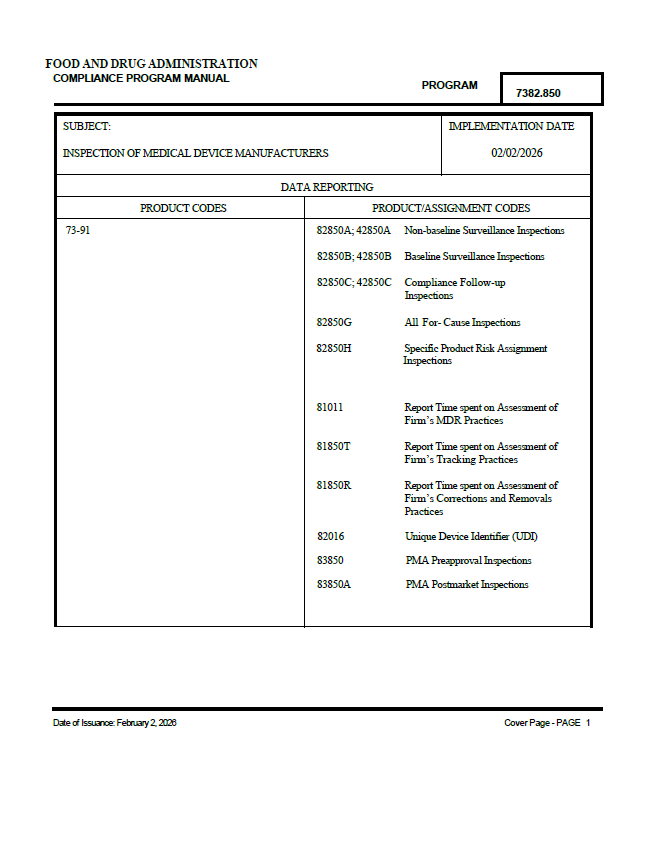
On 2 February 2026, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) implemented an updated Compliance Program for the Inspection of Medical Device Manufacturers (CP 7382.850). This program provides instructions to FDA field and Center staff for inspectional and enforcement activities related to medical device manufacturers.
The updated compliance program supersedes the previous Inspection of Medical Device Manufacturers program issued in September 2023, as well as the Medical Device PMA Preapproval and PMA Postmarket Inspections program issued in March 2012.
Scope of the compliance program
According to the FDA, Compliance Program 7382.850 applies to inspectional activities associated with:
The Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR) (21 CFR Part 820)
Premarket Approval (PMA) requirements
Medical Device Reporting (MDR) (21 CFR Part 803)
Medical Device Tracking (21 CFR Part 821)
Reports of Corrections and Removals (21 CFR Part 806)
Establishment Registration and Device Listing (21 CFR Part 807)
The Unique Device Identification (UDI) system (21 CFR Part 801 Subpart B and 21 CFR Part 830)
The Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP)
The program applies to manufacturers regulated by both the Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) and, where applicable, the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER).
Alignment with the Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR)
The compliance program reflects the implementation of the QMSR, which became effective on 2 February 2026. Under the QMSR, the FDA incorporated by reference ISO 13485:2016 and Clause 3 of ISO 9000:2015 into 21 CFR Part 820. The incorporated standards have the force and effect of law in the United States.
In addition to incorporating ISO 13485, the QMSR includes FDA-specific requirements intended to ensure consistency with other applicable FDA regulations.
Risk-based inspection approach
The updated inspection program establishes a risk-based inspection strategy. Inspections are conducted using a model that organises regulatory requirements into:
Six Quality Management System (QMS) Areas, and
Four Other Applicable FDA Requirements (OAFRs):
Medical Device Reporting
Reports of Corrections and Removals
Medical Device Tracking
Unique Device Identification
The inspection process is designed to evaluate compliance across the total product lifecycle, including design and development, production, postmarket activities, and change control.
The program places patients and users at the centre of the inspection model and requires investigators to use a manufacturer’s risk management documentation to identify and evaluate risks that could adversely impact patients or users.
Use of postmarket and quality data
The compliance program instructs FDA investigators to review multiple sources of information before and during inspections, including:
Medical Device Reports (MDRs)
Reports of Corrections and Removals
Complaint data
Postmarket surveillance information
UDI and GUDID records
This information is used to identify product risks and determine the scope and focus of inspections.
Inspection types and MDSAP
The program defines multiple types of inspections, including baseline surveillance, non-baseline surveillance, compliance follow-up, for-cause inspections, and PMA preapproval and postmarket inspections.
For manufacturers participating in the Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP), FDA may use MDSAP audit reports as a substitute for routine surveillance inspections. Manufacturers enrolled in MDSAP remain subject to for-cause and compliance follow-up inspections.
Responsibilities of manufacturers and contractors
The compliance program clarifies that finished device manufacturers retain overall responsibility for the safety and effectiveness of their devices, including activities performed by contract manufacturers and contract sterilizers. Contracted parties are subject to applicable requirements of the QMSR for the operations they perform.
Read the full document below.